FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
About ERS and it's maintenance
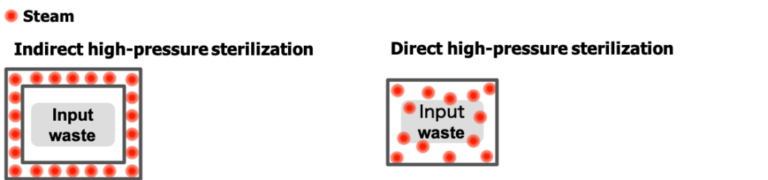
ERS fulfills 2 ways of sterilization; direct high-pressure sterilization and indirect high-pressure sterilization. The direct high-pressure sterilization is a common way which is also used for a conventional autoclave. In this direct way, moist heat in the form of saturated steam under pressure directly touches input waste inside the device. What makes ERS different from the conventional autoclave is the indirect sterilization method ERS can realize. This indirect method is exercised by heating ERS’s machine body by saturated steam at 2 atmosphere, keeping inside temperature to be 121 ℃ without wetting input waste.


No. The microbe planted inside the machine naturally grows and increases its population without replenishment.
Harmful germs such as Bacillus coli will be killed by heating at 65℃ through fermentation and drying process of ERS treatment.
Harmful germs such as Bacillus coli will be killed by heating at 65℃ through fermentation and drying process of ERS treatment.
A big difference between ERS process and common composting process is the time length of processing to generate fermented organic matter.


It is a high speed fermentation and drying technology using indigenous microbes and mechanical depressurization.


Two types of maintenance-Daily maintenance done internally and Annual checkup by the manufacturer.


